Discussion on flexibility analysis of PCB board-to-board connector
With automation and the Internet of Things changing the industrial environment, the demand for PCB board-to-board connectors for signal, data and power transmission and shielding from harsh environmental conditions is gradually increasing, because they are the key to developing further miniaturization potential and making industrial equipment more reliable and flexible. Although dust, vibration, high temperature and electromagnetic radiation put forward high requirements for electronic components, the flexibility of board-to-board connectors can meet these stringent requirements.
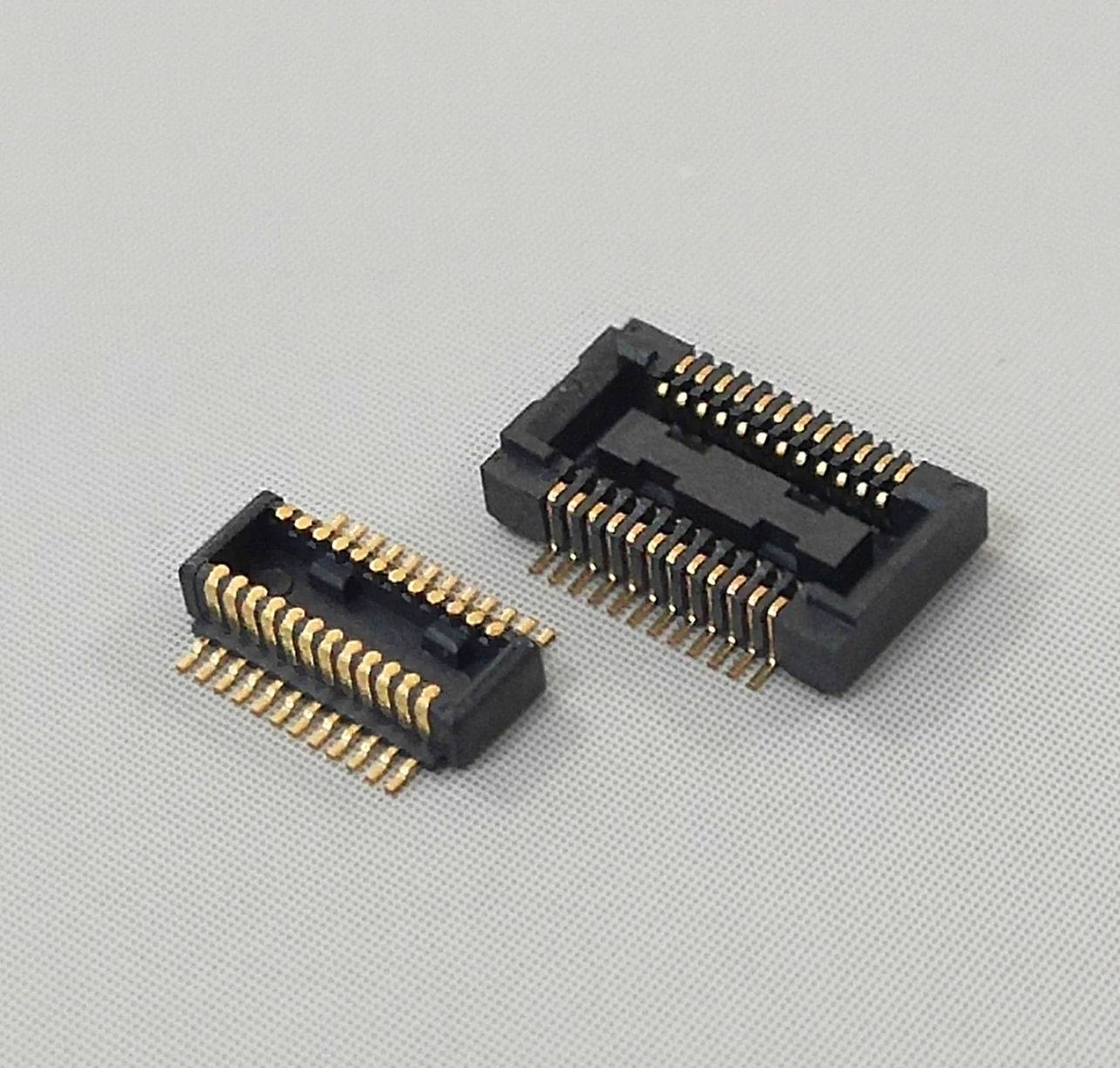
Many new board-to-board connectors can meet these stringent requirements. For example, the versions with spacing of 0.8mm and 1.27mm are usually very suitable for the internal connection between equipment and several printed circuit boards (PCBs), while the vertical version enables equipment manufacturers to realize sandwich, orthogonal or coplanar PCB layout, which supports more flexible electronic layout and thus has wider application adaptability.
Some newer board-to-board connectors can handle currents up to 1.4A and voltages up to 500VAC, and are suitable for applications with 12 to 80 connection points. Reverse polarity protection is especially important in board-to-board connectors with compact center line, because it can prevent contact interface from being damaged during mating and help to ensure long-term stable connection inside equipment. In this way, the insulation shells of many board-to-board connectors have special geometric shapes, which can prevent the male connector and the female connector from mismatching.
And the board-to-board connector with double-sided contacts can ensure the best contact force even under the maximum high impact force of 50g. This robust design can also perform up to 500 plugging and unplugging cycles without affecting electromechanical stability.